Links
Links let you add clickable URLs to tasks that appear in the Flyte UI. Use them to connect tasks to external tools like experiment trackers, monitoring dashboards or custom internal services.
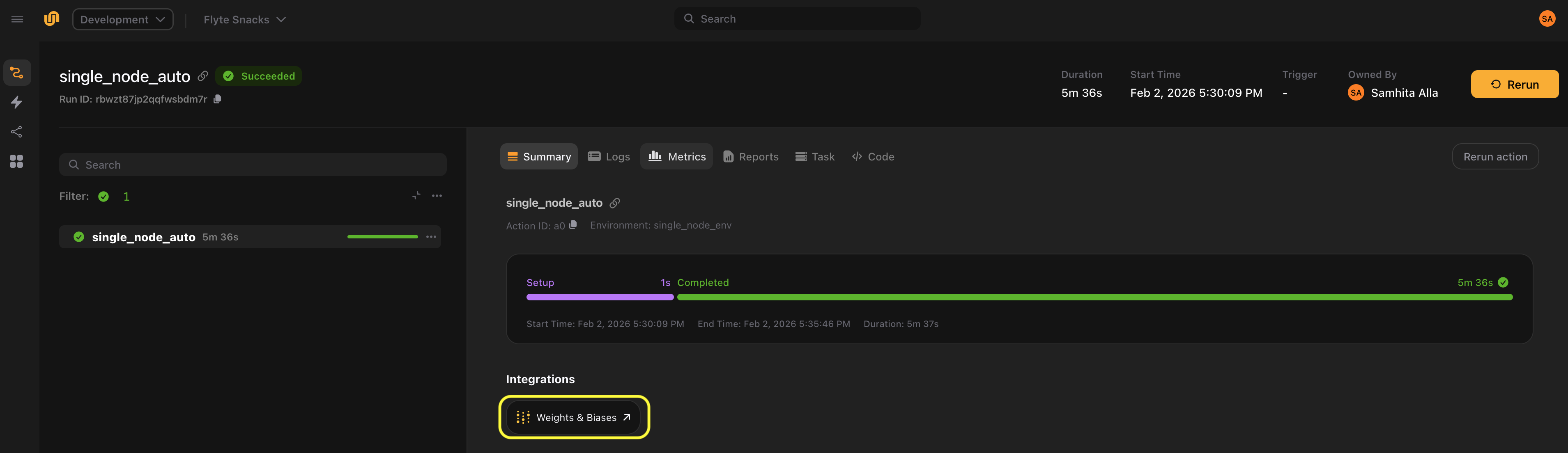
You can attach links to tasks in two ways:
- Statically in the task decorator with
links= - Dynamically at call time with
task.override(links=...)
Link is a Python
Protocol that you subclass to define how URLs are generated. The Weights & Biases plugin provides a
built-in link implementation as an example.
Creating a link
To create a link, subclass Link as a dataclass and implement the get_link() method. The method returns the URL string to display in the UI:
from dataclasses import dataclass
import flyte
from flyte import Link
@dataclass
class GrafanaLink(Link):
dashboard_url: str
name: str = "Grafana"
def get_link(
self,
run_name: str,
project: str,
domain: str,
context: dict,
parent_action_name: str,
action_name: str,
pod_name: str,
**kwargs,
) -> str:
return f"{self.dashboard_url}?var-pod={pod_name}"
env = flyte.TaskEnvironment(...)
@env.task(links=(GrafanaLink(dashboard_url="https://grafana.example.com/d/abc123"),))
def my_task() -> str:
return "done"The link appears as a clickable “Grafana” link in the Flyte UI for every execution of my_task.
Using execution metadata
The get_link() method receives execution metadata that you can use to construct dynamic URLs. Here’s an example modeled on the
built-in Wandb link that uses the context dict to resolve a run ID:
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import Optional
from flyte import Link
@dataclass
class Wandb(Link):
project: str
entity: str
id: Optional[str] = None
name: str = "Weights & Biases"
def get_link(
self,
run_name: str,
project: str,
domain: str,
context: dict[str, str],
parent_action_name: str,
action_name: str,
pod_name: str,
**kwargs,
) -> str:
run_id = self.id or context.get("wandb_id", run_name)
return f"https://wandb.ai/{self.entity}/{self.project}/runs/{run_id}"The name attribute controls the display label in the UI.
See the
get_link() API reference for more details. Note that action_name and pod_name are template variables ({{.actionName}} and {{.podName}}) that are populated by the backend at runtime.
Dynamic links with override
Use task.override(links=...) to set links at runtime. This is useful when link parameters depend on runtime values like run IDs or configuration:
import os
import flyte
from flyteplugins.wandb import Wandb
env = flyte.TaskEnvironment(...)
WANDB_PROJECT = "my-ml-project"
WANDB_ENTITY = "my-team"
@env.task
def train_model(config: dict) -> dict:
# Training logic here
return {"accuracy": 0.95}
@env.task
async def main(wandb_id: str) -> dict:
result = train_model.override(
links=(
Wandb(
project=WANDB_PROJECT,
entity=WANDB_ENTITY,
id=wandb_id,
),
)
)(config={"lr": 0.001})
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
flyte.init_from_config()
run = flyte.run(main, wandb_id="my-run-id")The override approach lets you attach links with values that are only known at runtime, such as dynamically generated run IDs.