Overriding parameters#
The with_overrides method allows you to specify parameter overrides on tasks,
subworkflows, and sub-launch plans at execution time.
This is useful when you want to change the behavior of a task, subworkflow, or sub-launch plan without modifying the original definition.
Task parameters#
When calling a task, you can specify the following parameters in with_overrides:
accelerator: Specify accelerators.cache_serialize: Enable cache serialization.cache_version: Specify the cache version.cache: Enable caching.container_image: Specify a container image.interruptible: Specify whether the task is interruptible.limits: Specify resource limits.name: Give a specific name to this task execution. This will appear in the workflow flowchart in the UI (see below.node_name: Give a specific name to the DAG node for this task. This will appear in the workflow flowchart in the UI (see below).requests: Specify resource requests.retries: Specify the number of times to retry this task.task_config: Specify a task config.timeout: Specify the task timeout.
For example, if you have a task that does not have caching enabled, you can use with_overrides to enable caching at execution time as follows:
my_task(a=1, b=2, c=3).with_overrides(cache=True)
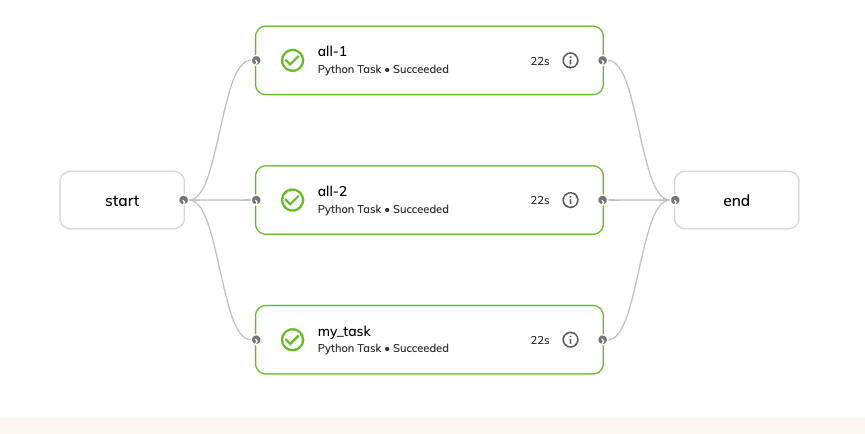
Using with_overrides with name and node_name#
Using with_overrides with name on a task is a particularly useful feature.
For example, you can use with_overrides(name="my_task") to give a specific name to a task execution, which will appear in the UI.
The name specified can be chosen or generated at invocation time without modifying the task definition.
@workflow
def wf() -> int:
my_task(a=1, b=1, c=1).with_overrides(name="all-1")
my_task(a=2, b=2, c=2).with_overrides(name="all-2")
return my_task(a=1, b=1, c=1)
The above code would produce the following workflow display in the UI:
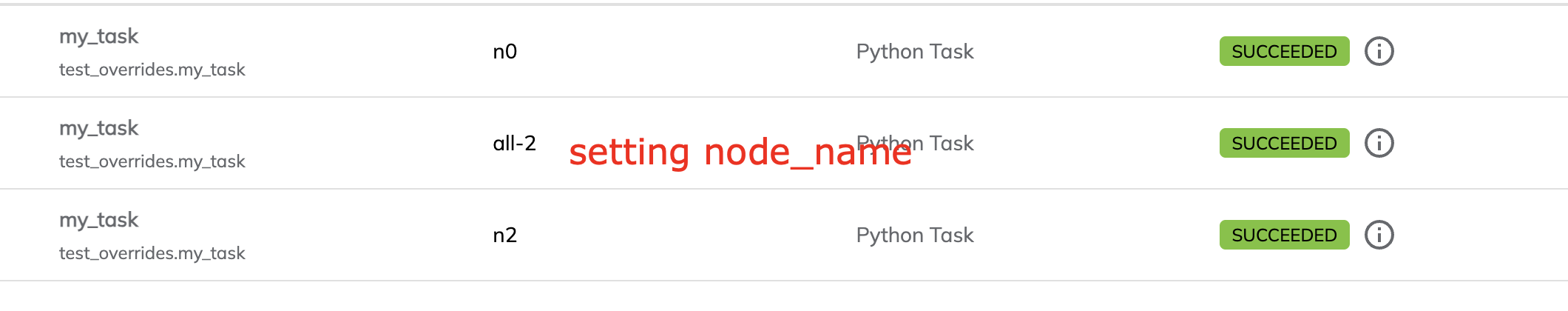
There is also a related parameter called node_name that can be used to give a specific name to the DAG node for this task.
The DAG node name is usually autogenerated as n0, n1, n2, etc. It appears in the node column of the workflow table.
Overriding node_name results in the autogenerated name being replaced by the specified name:
Subworkflow and sub-launch plan parameters#
When calling a workflow or launch plan from within a high-level workflow
(in other words, when invoking a subworkflow or sub-launch plan),
you can specify the following parameters in with_overrides:
cache_serialize: Enable cache serialization.cache_version: Specify the cache version.cache: Enable caching.